Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Optimize the shape of volumetric mesh¶
graphlow is a powerful tool for shape optimization, leveraging differentiable tensor-based geometric computations.
This example shows how to minimize surface area while constraining volume changes and vertex deformation.
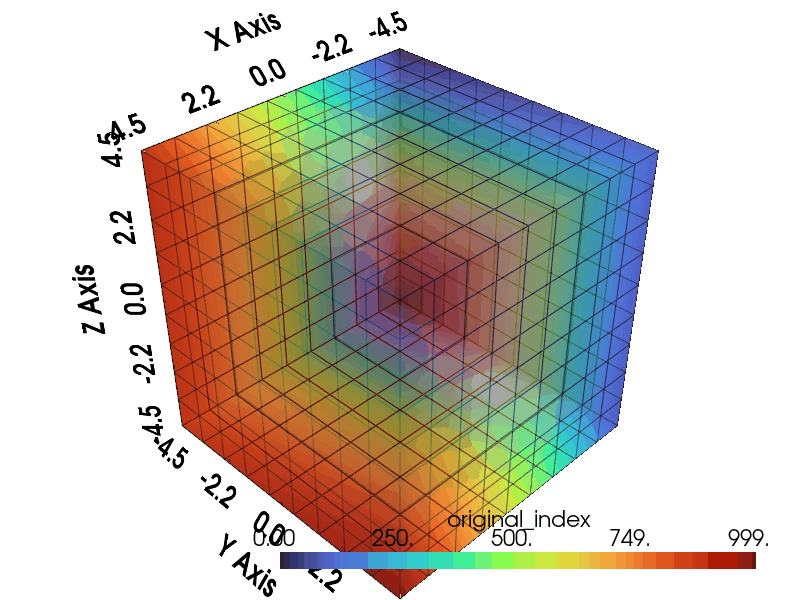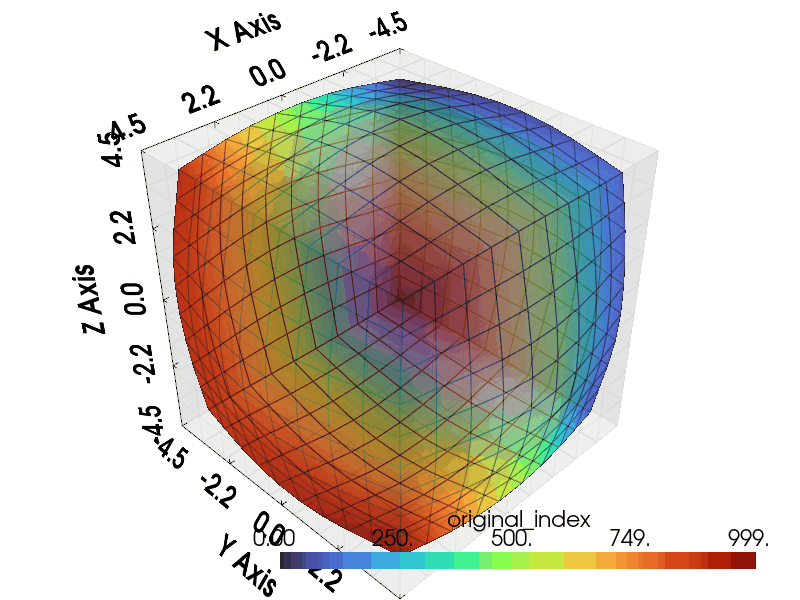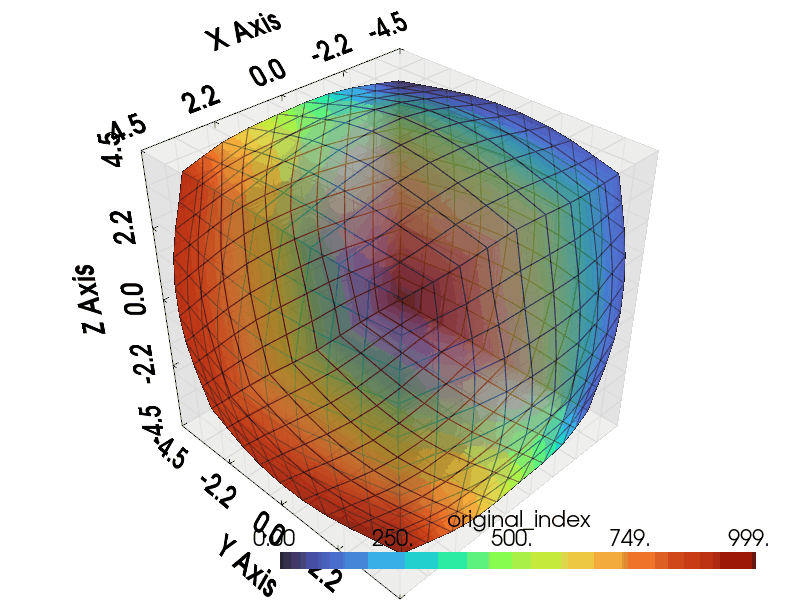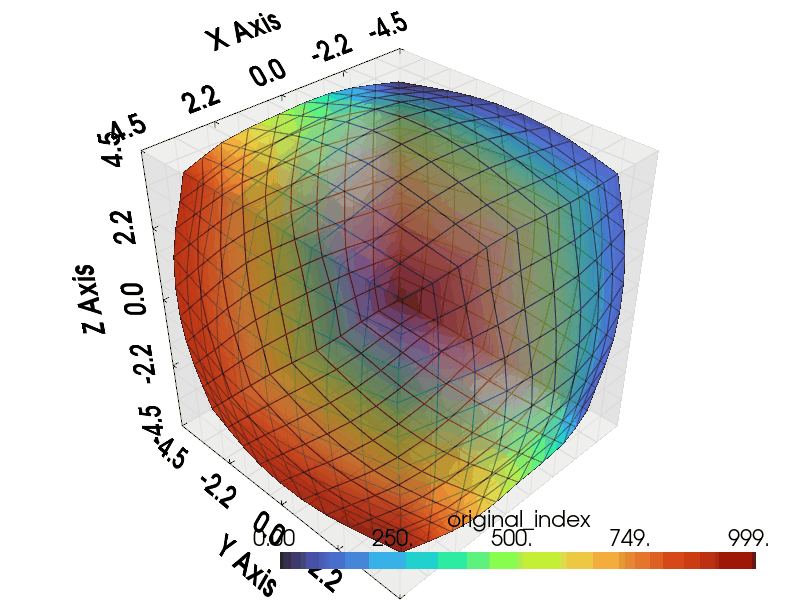
Import necessary modules including graphlow.
import itertools
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
import torch
import graphlow
Prepare a volumetric mesh¶
First, we define a function to generate grid data as the example mesh. If you wish to use your own mesh, you can skip this step.
def generate_grid(ni: int, nj: int, nk: int) -> pv.UnstructuredGrid:
n_cells = (ni - 1) * (nj - 1) * (nk - 1)
x = np.arange(ni, dtype=np.float32)
y = np.arange(nj, dtype=np.float32)
z = np.arange(nk, dtype=np.float32)
X, Y, Z = np.meshgrid(x, y, z, indexing="ij")
points = np.array([X.ravel(), Y.ravel(), Z.ravel()]).T
indices = np.arange(ni * nj * nk).reshape(ni, nj, nk)
hex_lists = []
for k in range(nk - 1):
for j in range(nj - 1):
for i in range(ni - 1):
# hex
v0 = indices[i, j, k]
v1 = indices[i + 1, j, k]
v2 = indices[i + 1, j + 1, k]
v3 = indices[i, j + 1, k]
v4 = indices[i, j, k + 1]
v5 = indices[i + 1, j, k + 1]
v6 = indices[i + 1, j + 1, k + 1]
v7 = indices[i, j + 1, k + 1]
hex_lists.append([8, v0, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7])
hex_cells = list(itertools.chain.from_iterable(hex_lists))
celltypes = np.full((n_cells), pv.CellType.HEXAHEDRON)
return pv.UnstructuredGrid(hex_cells, celltypes, points)
Define the cost function¶
To minimize surface area with constraints, we defined the cost function as follows:
weight_deformation_constraint = 1.0
weight_volume_constraint = 10.0
def cost_function(
mesh: graphlow.GraphlowMesh,
init_total_volume: float,
init_surface_total_area: float,
) -> torch.Tensor:
deformation = mesh.dict_point_tensor["deformation"]
surface = mesh.extract_surface(pass_point_data=True)
volumes = mesh.compute_volumes()
areas = surface.compute_areas()
total_volume = torch.sum(volumes)
total_area = torch.sum(areas)
if torch.any(volumes < 1e-3 * init_total_volume / mesh.n_cells):
return None
cost_area = total_area / init_surface_total_area
volume_constraint = (
(total_volume - init_total_volume) / init_total_volume
) ** 2
deformation_constraint = torch.mean(deformation * deformation)
return (
cost_area
+ weight_volume_constraint * volume_constraint
+ weight_deformation_constraint * deformation_constraint
)
Visualize¶
Following code generate gif plotter to visualize the result.
def create_gif_plotter(mesh: pv.UnstructuredGrid) -> pv.Plotter:
plotter = pv.Plotter(window_size=[800, 600])
init_mesh = mesh.copy()
plotter.add_mesh(init_mesh, show_edges=True, color="white", opacity=0.1)
plotter.add_mesh(
mesh, show_edges=True, lighting=False, cmap="turbo", opacity=0.8
)
plotter.open_gif("shape_optimization_result.gif")
plotter.show_bounds(init_mesh, location="outer")
plotter.camera_position = "iso"
return plotter
Once the cost function and the visualizing function are determined, the remaining step is to write the optimization code that updates the points and deformations
This is the example of the optimization code.
def optimize_shape(input_mesh: pv.UnstructuredGrid):
# Optimization setting
n_optimization = 2000
print_period = int(n_optimization / 100)
n_hidden = 64
deformation_factor = 1.0
lr = 1e-2
output_activation = torch.nn.Identity()
# Initialize
input_mesh.points = input_mesh.points - np.mean(
input_mesh.points, axis=0, keepdims=True
) # Center mesh position
mesh = graphlow.GraphlowMesh(input_mesh)
init_volumes = mesh.compute_volumes().clone()
init_total_volume = torch.sum(init_volumes)
init_points = mesh.points.clone()
init_surface = mesh.extract_surface()
init_surface_areas = init_surface.compute_areas().clone()
init_surface_total_area = torch.sum(init_surface_areas)
w1 = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.randn(3, n_hidden) / n_hidden**0.5)
w2 = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.randn(n_hidden, 3) / n_hidden**0.5)
params = [w1, w2]
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(params, lr=lr)
def compute_deformation(points: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
hidden = torch.tanh(torch.einsum("np,pq->nq", points, w1))
deformation = output_activation(torch.einsum("np,pq->nq", hidden, w2))
return deformation_factor * deformation
deformation = compute_deformation(init_points)
mesh.dict_point_tensor.update({"deformation": deformation}, overwrite=True)
mesh.copy_features_to_pyvista(overwrite=True)
mesh.pvmesh.points = mesh.points.detach().numpy()
plotter = create_gif_plotter(mesh.pvmesh)
plotter.write_frame()
# Optimization loop
print(f"\ninitial volume: {torch.sum(mesh.compute_volumes()):.5f}")
print(" i, cost")
for i in range(1, n_optimization + 1):
optimizer.zero_grad()
deformation = compute_deformation(init_points)
deformed_points = init_points + deformation
mesh.dict_point_tensor.update(
{"deformation": deformation}, overwrite=True
)
mesh.dict_point_tensor.update(
{"points": deformed_points}, overwrite=True
)
cost = cost_function(mesh, init_total_volume, init_surface_total_area)
if cost is None:
deformation_factor = deformation_factor * 0.9
print(f"update deformation_factor: {deformation_factor}")
continue
if i % print_period == 0:
print(f"{i:6d}, {cost:.5e}")
mesh.copy_features_to_pyvista(overwrite=True)
mesh.pvmesh.points = mesh.points.detach().numpy()
plotter.write_frame()
cost.backward()
optimizer.step()
plotter.close()
Run the optimization¶
Finally, we define the main function to run the optimization.
def main():
mesh = generate_grid(10, 10, 10)
optimize_shape(mesh)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
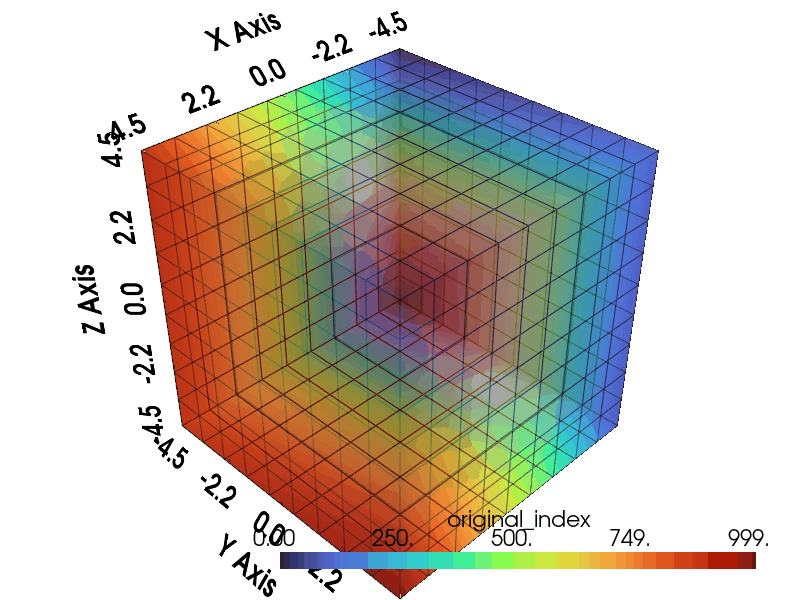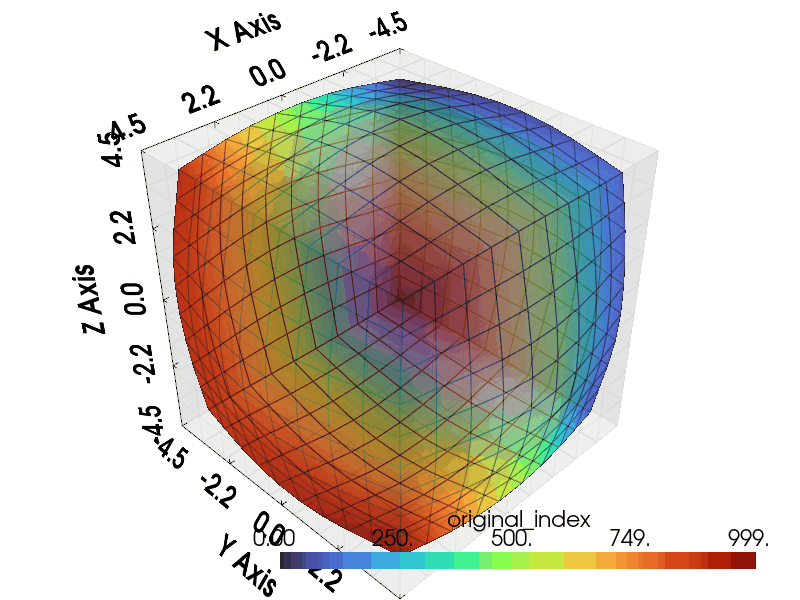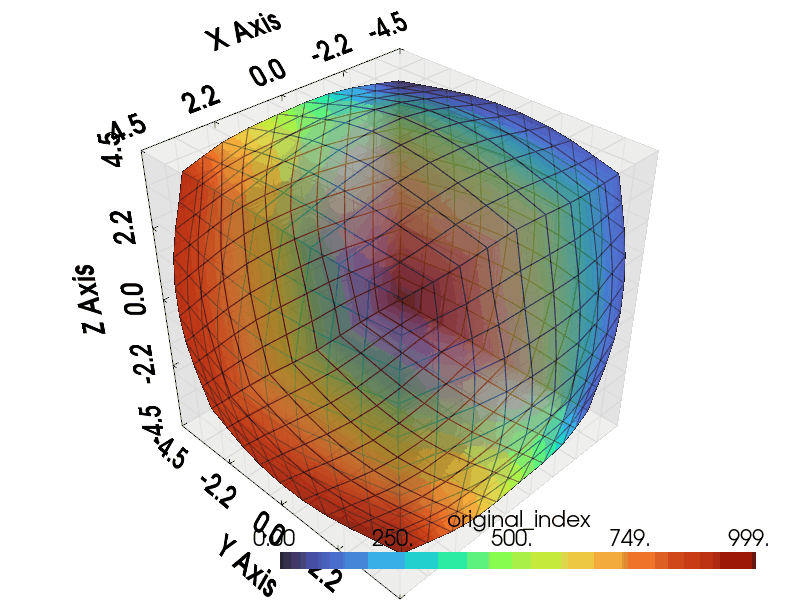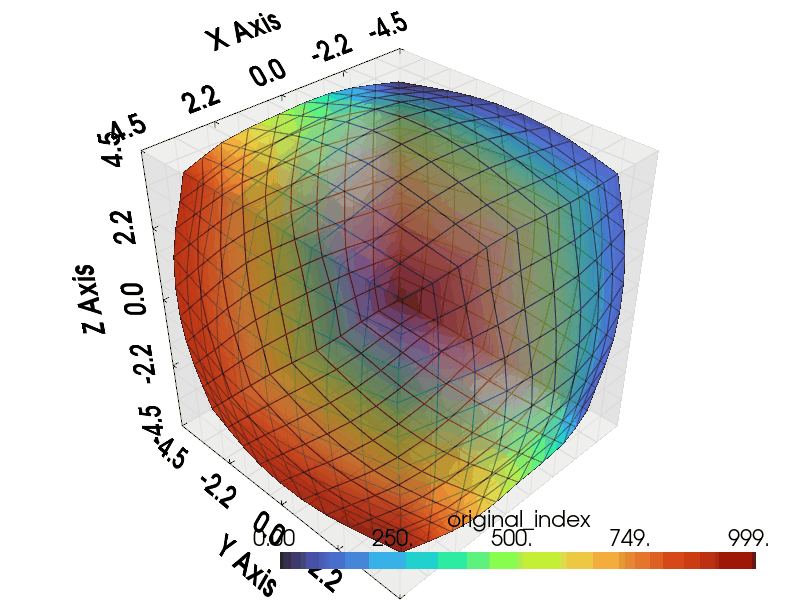
initial volume: 729.00000
i, cost
20, 1.03036e+00
40, 9.74918e-01
60, 9.57814e-01
80, 9.45589e-01
100, 9.36418e-01
120, 9.30070e-01
140, 9.26121e-01
160, 9.23669e-01
180, 9.21967e-01
200, 9.20648e-01
220, 9.19552e-01
240, 9.18605e-01
260, 9.17767e-01
280, 9.17014e-01
300, 9.16330e-01
320, 9.15702e-01
340, 9.15125e-01
360, 9.14590e-01
380, 9.14093e-01
400, 9.13630e-01
420, 9.15736e-01
440, 9.13180e-01
460, 9.12534e-01
480, 9.12377e-01
500, 9.12846e-01
520, 9.11651e-01
540, 9.11508e-01
560, 9.12426e-01
580, 9.10721e-01
600, 9.10423e-01
620, 9.17486e-01
640, 9.10091e-01
660, 9.09918e-01
680, 9.09485e-01
700, 9.09178e-01
720, 9.08861e-01
740, 9.08544e-01
760, 9.08328e-01
780, 9.17488e-01
800, 9.08949e-01
820, 9.07827e-01
840, 9.07530e-01
860, 9.07320e-01
880, 9.07142e-01
900, 9.06971e-01
920, 9.12378e-01
940, 9.06960e-01
960, 9.06892e-01
980, 9.06586e-01
1000, 9.06457e-01
1020, 9.06313e-01
1040, 9.06179e-01
1060, 9.06048e-01
1080, 9.05919e-01
1100, 9.29413e-01
1120, 9.09281e-01
1140, 9.05922e-01
1160, 9.05717e-01
1180, 9.05572e-01
1200, 9.05459e-01
1220, 9.05349e-01
1240, 9.05240e-01
1260, 9.05133e-01
1280, 9.05032e-01
1300, 9.29319e-01
1320, 9.07247e-01
1340, 9.05371e-01
1360, 9.04908e-01
1380, 9.04773e-01
1400, 9.04674e-01
1420, 9.04577e-01
1440, 9.04480e-01
1460, 9.04382e-01
1480, 9.04282e-01
1500, 9.04917e-01
1520, 9.08751e-01
1540, 9.05932e-01
1560, 9.04212e-01
1580, 9.03996e-01
1600, 9.03837e-01
1620, 9.03682e-01
1640, 9.03514e-01
1660, 9.03337e-01
1680, 9.03162e-01
1700, 9.02997e-01
1720, 9.02846e-01
1740, 9.06283e-01
1760, 9.07671e-01
1780, 9.03272e-01
1800, 9.02856e-01
1820, 9.02594e-01
1840, 9.02481e-01
1860, 9.02394e-01
1880, 9.02308e-01
1900, 9.02222e-01
1920, 9.02136e-01
1940, 9.02048e-01
1960, 9.01956e-01
1980, 9.01864e-01
2000, 9.05160e-01
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 41.550 seconds)